Prospective Evaluation Task
A Prospective Evaluation Task is an out-of-sample evaluation task that evaluates a model learned by observing its performance on new datasets,
- Context:
- Example(s):
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: Sampling Task, Out-of-group Bias, Learning Performance, Holdout Data, Machine Learning Algorithm, Bootstrap Sampling, Impact Evaluation, Counterfactual Analysis.
References
2020
- https://www.statsdirect.com/help/basics/prospective.htm
- QUOTE: ... A prospective study watches for outcomes, such as the development of a disease, during the study period and relates this to other factors such as suspected risk or protection factor(s). The study usually involves taking a cohort of subjects and watching them over a long period. The outcome of interest should be common; otherwise, the number of outcomes observed will be too small to be statistically meaningful (indistinguishable from those that may have arisen by chance). All efforts should be made to avoid sources of bias such as the loss of individuals to follow up during the study. Prospective studies usually have fewer potential sources of bias and confounding than retrospective studies. ...
2018
- (Wikipedia, 2018) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Impact_evaluation#Counterfactual_evaluation_designs Retrieved:2018-6-10.
- … The key challenge in impact evaluation is that the counterfactual cannot be directly observed and must be approximated with reference to a comparison group. There are a range of accepted approaches to determining an appropriate comparison group for counterfactual analysis, using either prospective (ex ante) or retrospective (ex post) evaluation design. Prospective evaluations begin during the design phase of the intervention, involving collection of baseline and end-line data from intervention beneficiaries (the 'treatment group') and non-beneficiaries (the 'comparison group'); they may involve selection of individuals or communities into treatment and comparison groups. Retrospective evaluations are usually conducted after the implementation phase and may exploit existing survey data, although the best evaluations will collect data as close to baseline as possible, to ensure comparability of intervention and comparison groups.
2017
- (Sammut & Webb, 2017) ⇒ (2017) Prospective Evaluation. In: Sammut C., Webb G.I. (eds) Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining. Springer, Boston, MA
- QUOTE: Prospective evaluation is an approach to Out-Of-Sample Evaluation whereby a model learned from historical data is evaluated by observing its performance on new data as they become available. Prospective evaluation is likely to provide a less biased estimation of future performance than evaluation on historical data.
1990
- (GAO, 1990) ⇒ US General Accounting Office. (1990). "Prospective Evaluation Methods: The prospective evaluation synthesis" (PDF).
- QUOTE: Among the prospective methods, we have chosen to focus here on the prospective evaluation synthesis. GAO developed the PES as a systematic method for meeting congressional requests for analyzing proposed legislation and helping identify top-priority problems. Other applications of the PES might be in the analysis of recommendations in draft GAO reports and in assessing the adequacy of proposed regulations.
This paper shows how the tools of evaluation methodology can be applied in order to provide the best possible information prospectively on the likely outcomes of proposed programs. A PES may be conducted through the comparison of policy or program alternatives, although it is also useful when focused on a single policy or program. It is easiest to perform when an adequate data base already exists. Fortunately, data bases concerning proposed programs frequently do exist, primarily because problems are rarely new. Often they have been addressed by past programs whose experiences can be drawn upon for the PES.
In essence, a PES is a combination of the following activities: (1) a careful, skilled textual analysis of a proposed program, designed to clarify the implied goals of that program and what is assumed to get results, (2) a review and synthesis of evaluation studies from similar programs, and (3) summary judgments of likely success, given a future context that is not too different from the past...
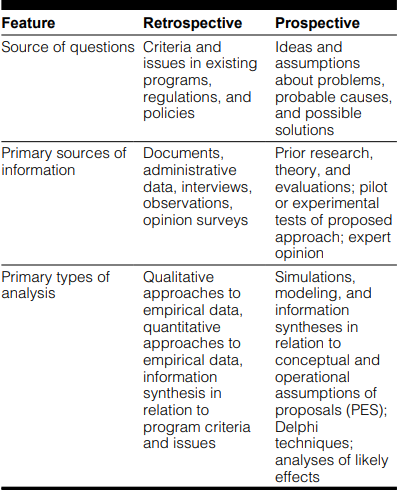
Table 1.2: Features of Retrospective and Prospective Methods
- QUOTE: Among the prospective methods, we have chosen to focus here on the prospective evaluation synthesis. GAO developed the PES as a systematic method for meeting congressional requests for analyzing proposed legislation and helping identify top-priority problems. Other applications of the PES might be in the analysis of recommendations in draft GAO reports and in assessing the adequacy of proposed regulations.