2011 CollectiveEntityLinkinginWebTex
- (Han et al., 2011) ⇒ Xianpei Han, Le Sun, and Jun Zhao. (2011). “Collective Entity Linking in Web Text: A Graph-based Method.” In: Proceedings of the 34th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in Information Retrieval. doi:10.1145/2009916.2010019
Subject Headings: Named Entity Disambiguation System, Collective Entity Linking System.
Notes
Cited By
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=%22Collective+entity+linking+in+web+text%3A+a+graph-based+method%22+2011
- http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2009916.2010019&preflayout=flat#citedby
Quotes
Author Keywords
Categories and Subject Descriptors
General Terms
Abstract
Entity Linking (EL) is the task of linking name mentions in Web text with their referent entities in a knowledge base. Traditional EL methods usually link name mentions in a document by assuming them to be independent. However, there is often additional interdependence between different EL decisions, i.e., the entities in the same document should be semantically related to each other. In these cases, Collective Entity Linking, in which the name mentions in the same document are linked jointly by exploiting the interdependence between them, can improve the entity linking accuracy.
This paper proposes a graph-based collective EL method, which can model and exploit the global interdependence between different EL decisions. Specifically, we first propose a graph-based representation, called Referent Graph, which can model the global interdependence between different EL decisions. Then we propose a collective inference algorithm, which can jointly infer the referent entities of all name mentions by exploiting the interdependence captured in Referent Graph. The key benefit of our method comes from: 1) The global interdependence model of EL decisions; 2) The purely collective nature of the inference algorithm, in which evidence for related EL decisions can be reinforced into high-probability decisions. Experimental results show that our method can achieve significant performance improvement over the traditional EL methods.
1. Introduction
(...)
The key issue is to correctly link the name mentions in a document with their referent entities in the knowledge base, which is usually referred to as Entity Linking (EL for short). For example, in Figure 1 an entity linking system should link the name mentions “Bulls”, “Jordan” and “Space Jam” to their corresponding referent entities Chicago Bulls, Michael Jordan and Space Jam in the knowledge base.
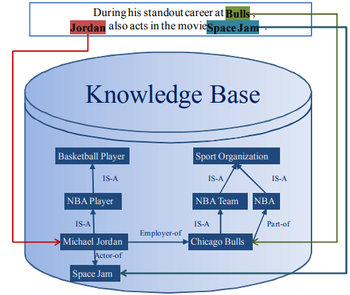
Figure 1. An illustration of entity linking.
5.1.4 Baselines
We compare our method with four state-of-the-art baselines:
Wikify!. This is the same EL method described in Mihalcea & Csomai [17], which is a standard Local Compatibility based method. The Wikify! computes the local compatibility using the contextual overlap between the name mention and the dictionary definitions of the entity(in their method, its Wikipedia page).
Cucerzan. This is the same method described in Cucerzan [4]. This is also a compatibility based method, but the compatibility between a name mention m and a candidate referent entity e is determined by two factors: the standard local compatibility and the relatedness between e and all other name mentions’ candidate referent entities in the same document.
M&W. This is the same EL method described in Milne & Witten [14, which is a state-of-the-art simple relational method. Given a name mention, M&W determines its referent entity by (mainly) comparing each of its candidate referent entity using the average relatedness between the entity and the name mention’s unambiguous contextual entities.
CSAW. This is the same EL system described in Kulkarni et al.[11. As described in Section 2, the CSAW is a collective EL method based on the pair-wise EL decision interdependence modeling.
Except for the CSAW, all other three baselines are designed only to link the important name mentions (i.e., key phrases) in a document. In our experiment, in order to compare the performances in a high recall, we push these systems’ recalls by reducing their importance thresholds of linked name mentions.
References
,
| Author | volume | Date Value | title | type | journal | titleUrl | doi | note | year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 CollectiveEntityLinkinginWebTex | Xianpei Han Le Sun Jun Zhao | Collective Entity Linking in Web Text: A Graph-based Method | 10.1145/2009916.2010019 | 2011 |