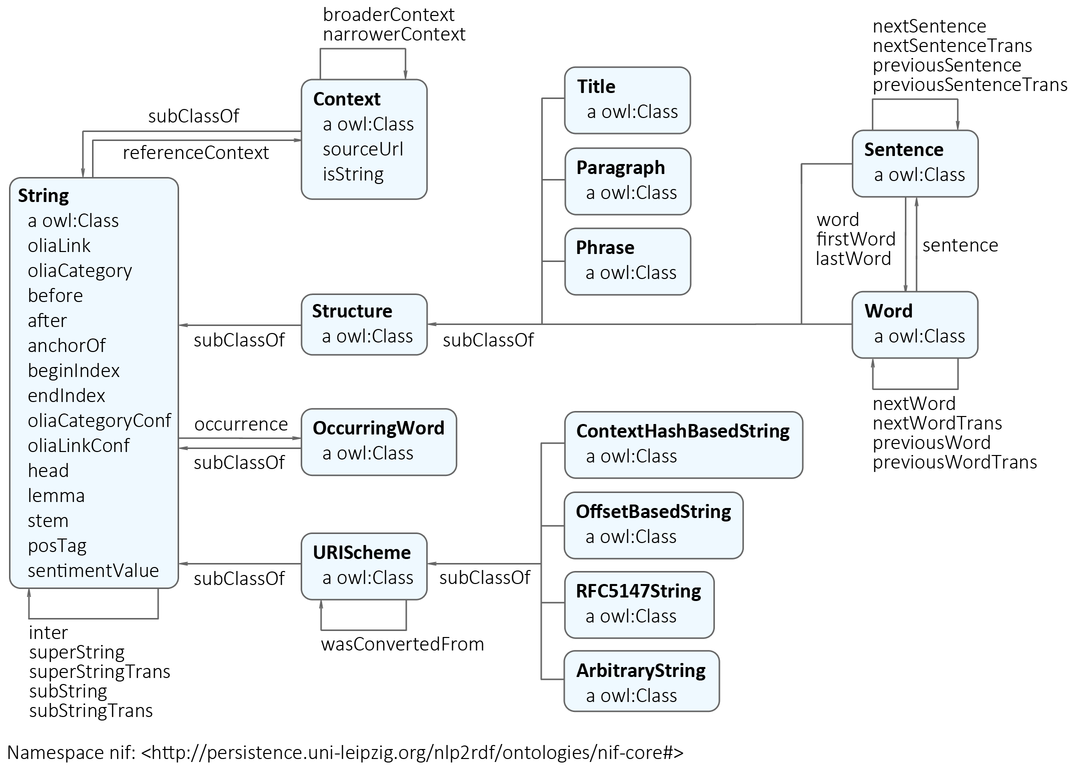
NLP Interchange (NIF) Format
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A NLP Interchange (NIF) Format is an NLP interchange format that ...
- Context:
- It can (typically) be a RDF/OWL-based format.
- Example(s):
- Counter-Example(s):
- See: LMF Lexical Markup Framework, MMoOn, DBpedia.
References
2016
- http://persistence.uni-leipzig.org/nlp2rdf/
- QUOTE: The NLP Interchange Format (NIF) is an RDF/OWL-based format that aims to achieve interoperability between Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools, language resources and annotations. NIF consists of specifications, ontologies and software (overview), which are combined under the version identifier "NIF 2.0", but are versioned individually.
This document contains pointers to all the important resources relevant for the NLP Interchange Format (NIF), Version 2.0. Although the road to complete interoperability is still long, NIF is already successful in providing best practices and a solid foundation for the most frequent use cases. This foundation is created by:
- Reusing existing standards such as RDF, OWL 2, the PROV Ontology, LAF (ISO 24612) and RFC 5147.
- Furthermore, NIF identifiers are used in the Internationalization Tag Set (ITS) Version 2.0
- All parts of NIF are royality-free and are published under an open license.
- NIF comprises a set of RDF vocabularies and ontologies, which have stable identifiers, persistent hosting, an open license and a community approved meaning.
- NIF publishes and maintains a set of specifications (NIF 2.0 Core Spec, Public Api Spec, Version Information ) with best practices, complementary implementations and examples on how to use the ontologies.
- NIF is driven by its open and weclome-to-join community project NLP2RDF, consisting of a mailing list, a GitHub Project and a blog web site
- NIF has received good uptake by industry, open-source projects and developers. We would like to thank all contributors in the attribution section
- … NIF 2.0 is a set of resources which constitute a major, not backward-compatible improvement upon the previous version NIF 1.0. Since NIF 2.0 is very diverse and it consists of specifications, ontologies, implementations and corpora. NIF is maintained by the NLP2RDF community project If you are interested in NLP2RDF, you can write emails to the nlp2rdf discussion list or sign up directly below:
- QUOTE: The NLP Interchange Format (NIF) is an RDF/OWL-based format that aims to achieve interoperability between Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools, language resources and annotations. NIF consists of specifications, ontologies and software (overview), which are combined under the version identifier "NIF 2.0", but are versioned individually.
2016
- https://site.nlp2rdf.org/
- Use UIMA and Gate, when:
- You need to annotate a really high amount of text on a daily basis.
- You already know, which tools and annotations you need and there are already adapters and plugins for UIMA or Gate .
- You want to solve few specialized task, such as identifying keywords or find certain facts. For this you are planning one custom application and you do not have any additional requirements for RDF or interoperability.
- Use NIF, when:
- You are using the LOD2 Stack
- The rest of your data is already in RDF.
- You want to query your text documents with SPARQL.
- You are not sure which tools to use and want to first try them and test the results.
- You have a fixed text collection (or a low daily throughput) and want to unlock the implicit meaning. The text can be processed once, saved as RDF and then transformed easily or queried in a triple store.
- You need annotations for several languages (multilingualism) in a uniform way
- Use UIMA and Gate, when: