Semantic System Model
A Semantic System Model is a meaning-based abstract knowledge representation model that encodes semantic structures to enable semantic understanding tasks and semantic interpretation processes.
- AKA: Semantic Model, Conceptual Model, Conceptualization, Semantic Representation, Meaning Model.
- Context:
- It can typically contain Semantic Model Concepts through semantic model structures.
- It can typically represent Semantic Model Relations via semantic model associations.
- It can typically enable Semantic Model Understanding through semantic model formalizations.
- It can typically support Semantic Model Reasoning via semantic model inferences.
- It can typically organize Semantic Model Knowledge through semantic model taxonomies.
- It can typically express Semantic Model Constraints via semantic model rules.
- ...
- It can often provide Semantic Model Interoperability through semantic model alignments.
- It can often facilitate Semantic Model Knowledge Transfer via semantic model mappings.
- It can often enable Semantic Model Discovery through semantic model mining.
- It can often preserve Semantic Model Expertise via semantic model encodings.
- It can often support Semantic Model Validation through semantic model consistency checks.
- ...
- It can range from being an Informal Semantic System Model to being a Formal Semantic System Model, depending on its semantic system model formalization degree.
- It can range from being a Domain-Specific Semantic System Model to being a General Semantic System Model, depending on its semantic system model scope.
- It can range from being a Rule-Based Semantic System Model to being a Statistical Semantic System Model, depending on its semantic system model approach.
- It can range from being a Static Semantic System Model to being a Dynamic Semantic System Model, depending on its semantic system model evolution capability.
- It can range from being a Human-Oriented Semantic System Model to being a Machine-Oriented Semantic System Model, depending on its semantic system model target audience.
- ...
- It can integrate with System Models as semantic system model layers.
- It can support Physical System Models through semantic system model abstractions.
- It can differ from Logical Data Models through semantic system model meaning focus.
- It can utilize Semantic Model Languages for semantic system model expressions.
- It can be created by Semantic Model Creation Systems using semantic model methodologies.
- ...
- Example(s):
- Knowledge Representation Semantic System Models, such as:
- Ontology, providing semantic system model formal specifications.
- Knowledge Base, storing semantic system model structured information.
- Semantic Network, mapping semantic system model concept relationships.
- Knowledge Graph, representing semantic system model entity connections.
- Topic Map, organizing semantic system model subject associations.
- Domain-Specific Semantic System Models, such as:
- Enterprise Data Model, capturing semantic system model business concepts.
- Finance-Related Ontology, encoding semantic system model financial knowledge.
- Biological Ontology, classifying semantic system model organism taxonomies.
- Medical Ontology, structuring semantic system model clinical concepts.
- Contract AI CDM, organizing semantic system model legal concepts.
- Cognitive Semantic System Models, such as:
- Mental Model, representing semantic system model cognitive structures.
- Conceptual Structure, organizing semantic system model abstract concepts.
- User Mental Model, capturing semantic system model interaction understanding.
- Shared Mental Model, enabling semantic system model team coordination.
- Cognitive Map, visualizing semantic system model spatial relationships.
- Data-Oriented Semantic System Models, such as:
- Conceptual Data Model, defining semantic system model data meanings.
- Database Schema, structuring semantic system model data relationships.
- Metadata Model, describing semantic system model data characteristics.
- Semantic Database Model, encoding semantic system model data semantics.
- Entity-Relationship Model, mapping semantic system model entity connections.
- Language-Based Semantic System Models, such as:
- Lexical Semantic Model, capturing semantic system model word meanings.
- Semantic Word Model, representing semantic system model lexical relationships.
- Latent Semantic Model, discovering semantic system model hidden patterns.
- Semantic Vector Space Model, encoding semantic system model numerical representations.
- Distributional Semantic Model, deriving semantic system model contextual meanings.
- Formal Logic Semantic System Models, such as:
- Description Logic Model, enabling semantic system model formal reasoning.
- First-Order Logic Model, expressing semantic system model predicate logic.
- Modal Logic Model, capturing semantic system model possibility reasoning.
- Formal Semantic Model, providing semantic system model mathematical foundations.
- Temporal Logic Model, representing semantic system model time-based reasoning.
- Process-Oriented Semantic System Models, such as:
- Business Process Model, capturing semantic system model workflow semantics.
- Workflow Model, structuring semantic system model activity sequences.
- Service Model, defining semantic system model service capabilities.
- Event Model, representing semantic system model occurrence patterns.
- ...
- Knowledge Representation Semantic System Models, such as:
- Counter-Example(s):
- Physical Model, which provides tangible representations rather than semantic system model abstractions.
- Simulation Model, which emphasizes dynamic execution rather than semantic system model representations.
- Syntactic Model, which captures structural forms rather than semantic system model meanings.
- Statistical Model, which identifies numerical patterns without semantic system model interpretations.
- Procedural Model, which defines operational steps rather than semantic system model concepts.
- See: System Model, Knowledge Representation Model, Conceptual Structure, Semantic Network.
References
2023
- (Wikipedia, 2023) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conceptual_model Retrieved:2023-7-23.
- A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people know, understand, or simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, a physical model focuses on a physical object such as a toy model that may be assembled and made to work like the object it represents.
The term may refer to models that are formed after a conceptualization or generalization process. Conceptual models are often abstractions of things in the real world, whether physical or social. Semantic studies are relevant to various stages of concept formation. Semantics is basically about concepts, the meaning that thinking beings give to various elements of their experience.
- A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people know, understand, or simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, a physical model focuses on a physical object such as a toy model that may be assembled and made to work like the object it represents.
2023
- (Wikipedia, 2023) ⇒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conceptual_model#Conceptual_model_vs Retrieved:2023-7-23.
- Conceptual Models and semantic models have many similarities, however the way they are presented, the level of flexibility and the use are different.
Conceptual models have a certain purpose in mind, hence the core semantic concepts are predefined in a so-called meta model. This enables a pragmatic modelling but reduces the flexibility, as only the predefined semantic concepts can be used. Samples are flow charts for process behaviour or organisational structure for tree behaviour.
Semantic models are more flexible and open, and therefore more difficult to model. Potentially any semantic concept can be defined, hence the modelling support is very generic. Samples are terminologies, taxonomies or ontologies.
In a concept model each concept has a unique and distinguishable graphical representation, whereas semantic concepts are by default the same.
In a concept model each concept has predefined properties that can be populated, whereas semantic concepts are related to concepts that are interpreted as properties.
In a concept model operational semantic can be built-in, like the processing of a sequence, whereas a semantic model needs explicit semantic definition of the sequence.
The decision if a concept model or a semantic model is used, depends therefore on the "object under survey", the intended goal, the necessary flexibility as well as how the model is interpreted. In case of human-interpretation there may be a focus on graphical concept models, in case of machine interpretation there may be the focus on semantic models.
- Conceptual Models and semantic models have many similarities, however the way they are presented, the level of flexibility and the use are different.
2015
- (Wikipedia, 2015) ⇒ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conceptual_schema Retrieved:2015-8-4.
- A conceptual schema is a high-level description of a business's informational needs. It typically includes only the main concepts and the main relationships among them. Typically this is a first-cut model, with insufficient detail to build an actual database. ...
2013
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conceptual_model
- In the most general sense, a model is anything used in any way to represent anything else. Some models are physical objects, for instance, a toy model which may be assembled, and may even be made to work like the object it represents. Whereas, a conceptual model is a model that exists only in the mind. Conceptual models are used to help us know and understand the subject matter they represent.
The term conceptual model may be used to refer to models which are formed after a conceptualization process in the mind. ...
- In the most general sense, a model is anything used in any way to represent anything else. Some models are physical objects, for instance, a toy model which may be assembled, and may even be made to work like the object it represents. Whereas, a conceptual model is a model that exists only in the mind. Conceptual models are used to help us know and understand the subject matter they represent.
2013
- Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conceptual_model_(computer_science)
- A mental model captures ideas in a problem domain, while a conceptual model represents 'concepts' (entities) and relationships between them. A Conceptual model in the field of computer science is also known as a domain model. Conceptual modeling should not be confused with other modeling disciplines such as data modelling, logical modelling and physical modelling. The conceptual model is explicitly chosen to be independent of design or implementation concerns, for example, concurrency or data storage. The aim of a conceptual model is to express the meaning of terms and concepts used by domain experts to discuss the problem, and to find the correct relationships between different concepts. The conceptual model attempts to clarify the meaning of various, usually ambiguous terms, and ensure that problems with different interpretations of the terms and concepts cannot occur. Such differing interpretations could easily cause confusion amongst stakeholders, especially those responsible for designing and implementing a solution, where the conceptual model provides a key artifact of business understanding and clarity. Once the domain concepts have been modeled, the model becomes a stable basis for subsequent development of applications in the domain. The concepts of the conceptual model can be mapped into physical design or implementation constructs using either manual or automated code generation approaches. The realization of conceptual models of many domains can be combined to a coherent platform.
A conceptual model can be described using various notations, such as UML or OMT for object modelling, or IE or IDEF1X for Entity Relationship Modelling. In UML notation, the conceptual model is often described with a class diagram in which classes represent concepts, associations represent relationships between concepts and role types of an association represent role types taken by instances of the modelled concepts in various situations. In ER notation, the conceptual model is described with an ER Diagram in which entities represent concepts, cardinality and optionality represent relationships between concepts. Regardless of the notation used, it is important not to compromise the richness and clarity of the business meaning depicted in the conceptual model by expressing it directly in a form influenced by design or implementation concerns.
This is often used for defining different processes in a particular Company or Institute.
- A mental model captures ideas in a problem domain, while a conceptual model represents 'concepts' (entities) and relationships between them. A Conceptual model in the field of computer science is also known as a domain model. Conceptual modeling should not be confused with other modeling disciplines such as data modelling, logical modelling and physical modelling. The conceptual model is explicitly chosen to be independent of design or implementation concerns, for example, concurrency or data storage. The aim of a conceptual model is to express the meaning of terms and concepts used by domain experts to discuss the problem, and to find the correct relationships between different concepts. The conceptual model attempts to clarify the meaning of various, usually ambiguous terms, and ensure that problems with different interpretations of the terms and concepts cannot occur. Such differing interpretations could easily cause confusion amongst stakeholders, especially those responsible for designing and implementing a solution, where the conceptual model provides a key artifact of business understanding and clarity. Once the domain concepts have been modeled, the model becomes a stable basis for subsequent development of applications in the domain. The concepts of the conceptual model can be mapped into physical design or implementation constructs using either manual or automated code generation approaches. The realization of conceptual models of many domains can be combined to a coherent platform.
2009
- (WordNet, 2009) ⇒ http://wordnetweb.princeton.edu/perl/webwn?s=conceptualization
- S: (n) conceptualization, conceptualisation, formulation (inventing or contriving an idea or explanation and formulating it mentally)
- S: (n) conceptualization, conceptualisation, conceptuality (an elaborated concept)
- http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/conceptualization
- 1. the act of conceptualizing, or something conceptualized
- (WordNet, 2009) ⇒ http://wordnetweb.princeton.edu/perl/webwn?s=conceptualize
- S: (v) gestate, conceive, conceptualize, conceptualise (have the idea for) "He conceived of a robot that would help paralyzed patients"; "This library was well conceived"
- http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/conceptualize#Verb
- 1. To interpret a phenomenon by forming a concept
- 2. To conceive the idea for something
2007
- (Obitko, 2007) ⇒ Marek Obitko. (2007). “Translations between Ontologies in Multi-Agent Systems", Ph.D. dissertation, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague. http://obitko.com/tutorials/ontologies-semantic-web/specification-of-conceptualization.html
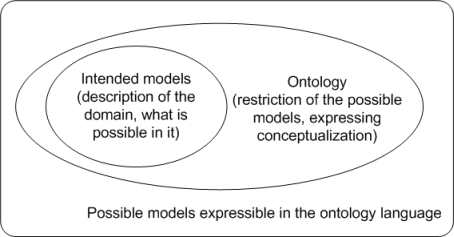
- A conceptualization can be defined as an intensional semantic structure that encodes implicit knowledge constraining the structure of a piece of a domain. Ontology is a (partial) specification of this structure, i.e., it is usually a logical theory that expresses the conceptualization explicitly in some language. Conceptualization is language independent, while ontology is language dependent. The use can be illustrated in the figure below - it shows how an ontology restricts (i.e., defines) possible use of constructs used in the description of the domain. Notice that ontology does not have to express all the possible constraints - the level of details in conceptualization depends on the requirements of the intended application and expressing conceptualization in ontology in addition depends on the used ontology language.
1993
- (Gruber, 1993) ⇒ Tom Gruber. (1993). “A translation approach to portable ontology specifications." Knowledge Acquisition, 2(5):199--220.
- A conceptualization is an abstract, simplified view of the world that we wish to represent for some purpose. Every knowledge base, knowledge-based system, or knowledge-level agent is committed to some conceptualization, explicitly or implicitly. An ontology is an explicit specification of a conceptualization..
1983
- (Norman, 1983) ⇒ Donald A. Norman. (1983). “Some Observations on Mental Models." Mental models 7, no. 112
- … A conceptual model is invented to provide an appropriate representation of the target system, appropriate in the sense of being accurate, consistent, and complete. …